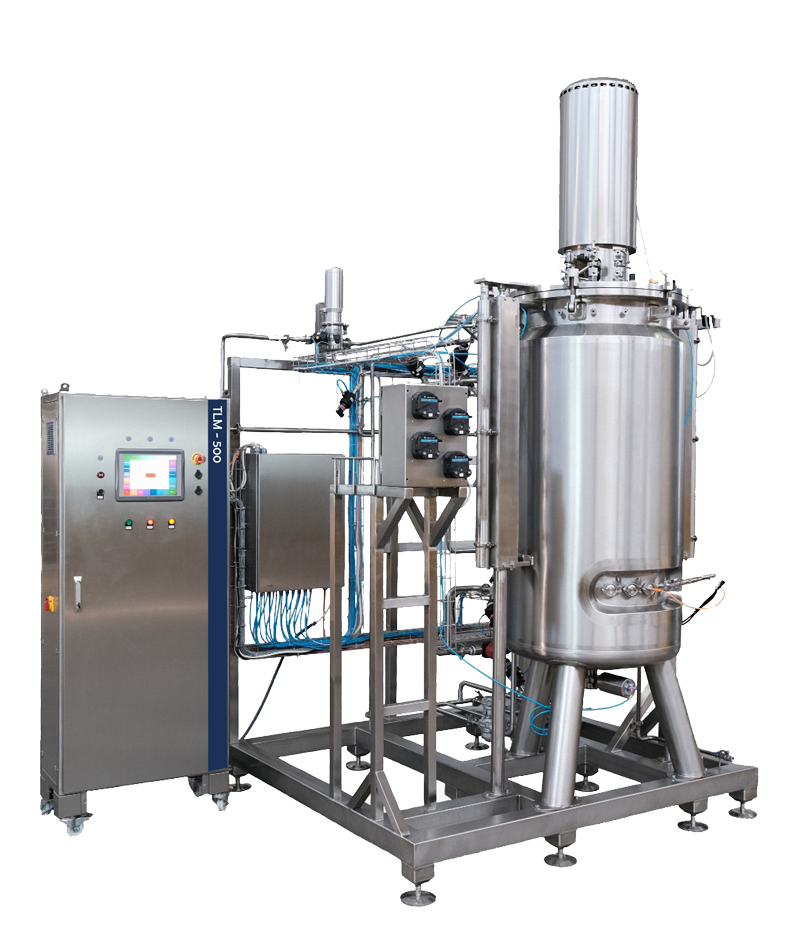
Probiotics
Probiotics are growing in interest in the food industry due to their health benefits. The market for probiotics worldwide exceeded $2 billion in 2018 and is anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 7.3% from 2019 to 2026. The most frequent genera of probiotics comprise Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Saccharomyces, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Escherichia, and Bacillus, with Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species most frequently employed. Food production involves the use of probiotics, as they critically alleviate conditions related to ailments such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), infectious diseases, and allergies. Bioreactors and fermenters are indispensable instruments for producing probiotics, eliminating cultivation obstacles. The production process of probiotics presents significant challenges and requires a high level of overages to guarantee that each strain meets the supplement label’s claimed characteristics. Therefore, selecting appropriate bacterial strains is imperative, considering their health benefits, resilience, and survival capacity in diverse conditions.
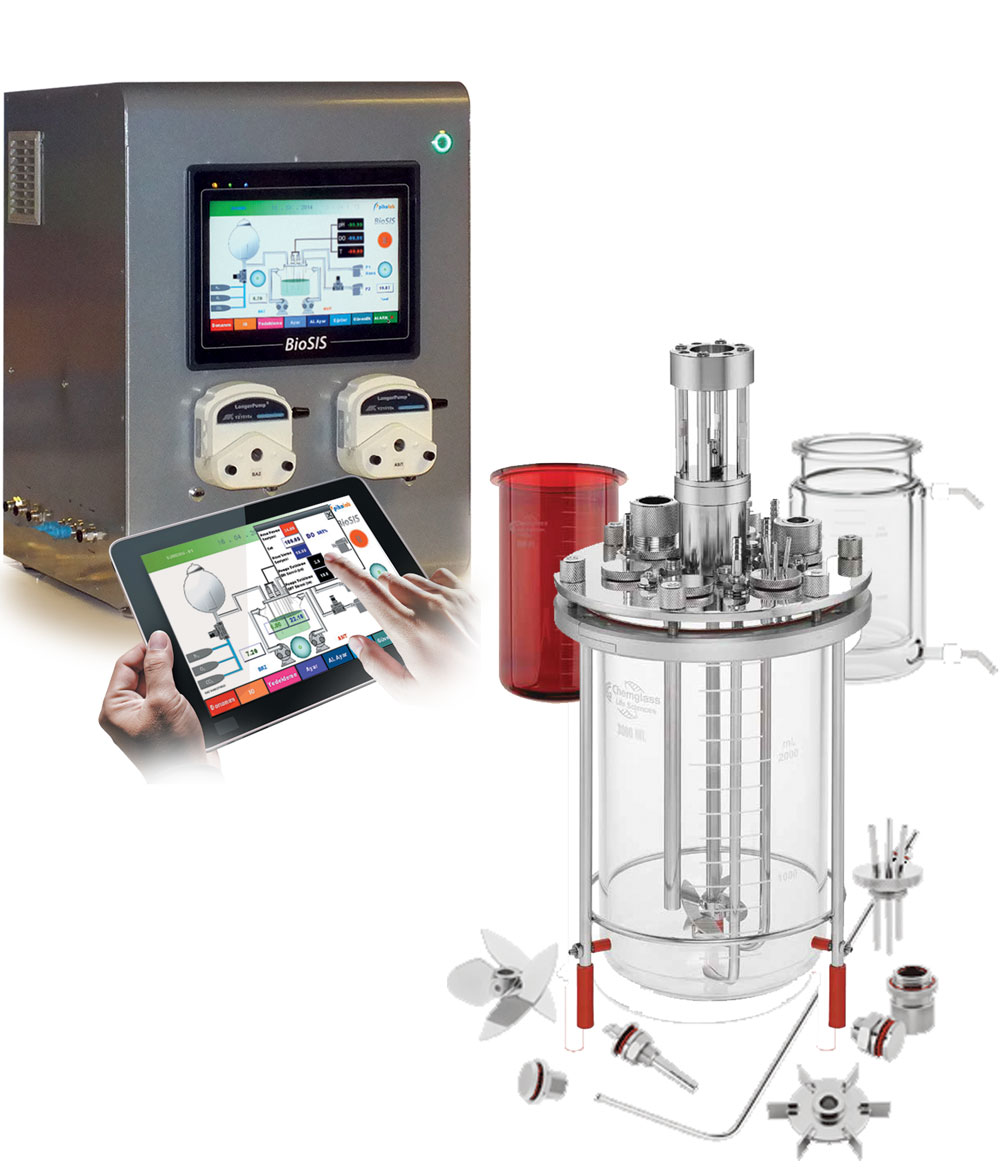

Small Scale Bioreactos
Pilot Scale Bioreactors
